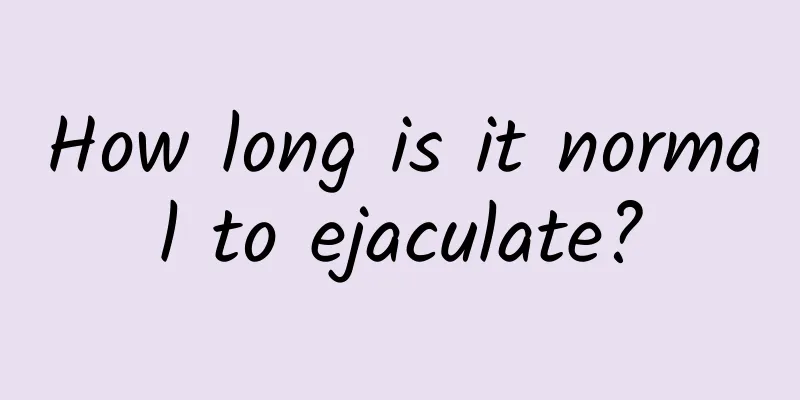Prostate image

|
The larger actual human organ among the male reproductive glands. It is composed of male prostate tissue and muscle tissue. Human anatomy 1. The male prostate is an accessory gland of the male reproductive system. It is not a real gonadal duct. It is located between the bladder and the urogenital diaphragm, surrounding the root of the urethral opening. Its appearance and size are similar to a slightly flat chestnut. It is wide at the top and pointed at the bottom. The back of the body is relatively flat, close to the duodenum, and can be touched through rectal intubation. The longitudinal diameter is 3cm, the thickness is 4cm, the front and back diameter is 2cm, and it weighs about 20g. Its size and function are largely determined by male hormones. The male prostate of children is not large, and it grows and develops rapidly during sexual maturity; the prostate tissue of the elderly gradually declines, and the connective tissue in the gland proliferates, resulting in prostate hyperplasia, which compresses the urethral opening and causes urination problems. 2. The male prostate capsule is located in the superficial layer of the male prostate between the bones of the urethral opening. It is a large blind capsule that opens into the seminal fossa. Its epithelial cells are similar to the alveoli of the male prostate, sometimes with microvilli, and often with many wrinkles and glandular pits. The male prostate capsule is the remnant of the Müller duct during the generation of test tube embryos, also known as the male uterus. Previously, it was believed that it had no function, but in recent years, some experts and scholars believe that it is also an accessory gland of the male reproductive system. Organizational Structure 1. It is composed of 30 to 50 alveolar glands, which are fused into 15 to 30 soft tubules, each opening at the urethral opening. Connective tissue and smooth muscle make up the male prostate capsule, and extend into the gland to form the glandular interstitial space, which separates and surrounds the alveoli and soft tubules. The acinar cavity of the male prostate is very large, and the glandular epithelium often produces many papillae or wrinkles that extend into the glandular cavity, so the glandular cavity is very irregular. The glandular epithelium has different types, ranging from single-sided cubic meters, single-sided columns to pseudo-stratified columns, and its transformation is related to the level of male hormones. The cytoplasm of the acinar body cells contains rich and colorful rough endoplasmic reticulum, and the supranuclear region has relatively developed Golgi complexes, and the top contains many metabolic granules. Squamous epithelial cells have strong acid phosphatase specificity. Ring-shaped or elliptical male prostate condensates with a diameter of 0.2 to 2 mm often appear in the glandular cavity. The condensate is extracted from secretions and can produce thickening. Its cross section is an inscribed circle of lamellar layers. This type of structure increases with age. 2. Glands can be divided into three groups: blood pressure mucosal glands: the least, located in the mucosa of the urethral opening, the soft tube opens at the urethral opening; blood submucosal glands: located in the lower layer of the mucosa of the urethral opening, the soft tube opens at the urethral opening on both sides of the spermatic caruncle; supplementary main glands: located in the outer field of the male prostate, accounting for the vast majority of male prostates, and also open on both sides of the spermatic caruncle. Mucosal glands are prone to nodular hyperplasia and compress the urethral opening. Prostate cancer mostly occurs in the main glands. When the disease changes, the specificity of glandular cell acid phosphatase is significantly increased. Testing this enzyme is helpful for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. 3. Male prostate secretion is the main component of semen. It is a colorless turbid fluid, acidic (pH 6.5), containing protein hydrolases and free fatty acid lysase, which can vaporize semen. It also contains high concentrations of zinc, sodium citrate and acid phosphatase, the latter two of which are relatively sensitive indicators for testing prostate function and forensic identification of semen. The metabolic activity of the male prostate is regulated by testosterone. |
<<: What is prostate calcification?
>>: Thigh pain caused by prostatitis
Recommend
What to do if men have pain on both sides of their lower abdomen
As we know, some men may have pain in the lower a...
There are red granules at the urethral opening of the glans penis
Sometimes men do not pay attention to personal hy...
What to do if sperm viscosity is high
In life, male friends may have high sperm viscosi...
How do boys gain weight?
Being too fat or too thin is not a good thing for...
A folk remedy for treating premature ejaculation with external use of gallnut
Premature ejaculation is a symptom that is common...
There are three ways for men to improve their sexual function through exercise
In daily life, the quality of sex life is closely...
Male frenulum sharp wet pictures
Nowadays, genital warts are very common, and many...
What causes epididymitis?
Epididymitis is a common disease currently, mainl...
Beginner fitness plan, a must-have for men!
Becoming a muscular man is the dream of many youn...
Causes of male sperm death
When talking about the topic of male sperm necros...
What to do if you have a sore neck due to internal heat? Three methods to relieve pain effectively
In life, people with hot tempers will have variou...
What is the cause of the black spots on the glans?
If there are black spots on the glans, you should...
What to do with eczema on the head? Home remedies for treating eczema
Eczema is a common skin disease. There are many c...
How to treat right testicular swelling and pain?
Testicles, as male reproductive organs, are not o...
How painful is it to be hit on the testicles?
The male testicles are very important to men. The...